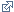
Cystitis
Cystitis is inflammation of the bladder. This inflammation is mostly due to a urinary infection caused by a bacterium from in the digestive system which contaminates the genitals and the perineal region to ascend via the urethra. It is prevalent in women.
Causes
The majority of the infections tend to be caused by the bacterium E. coli (Escherichia coli).
- In sexual intercourse: Taking a long time to urinate after intercourse, use of spermicides, use of diaphragms (which contain spermicides), among others are factors that increase the risk of urinary infections.
- Hormonal factors after the menopause and pregnancy.
- Alterations to the urinary system.
- Blockages in the urinary tracts: Caused by stones in the bladder, benign prostatic hyperplasia, etc.
- Prolonged use of probes: Probes are a common route for the passage of bacteria through the urethra. For this reason, it is indicated to limit them to the time strictly necessary.
- Structural changes to the bladder wall: In these cases, chronic cystitis usually occurs.
- Immune system: When the immune system is weak for whatever reason (diabetes, cancer treatments, HIV, etc.) any small bacterial attack will spread easily.
- Drug-induced cystitis: Drugs such as ifosfamide and cyclophosphamide (used in chemotherapy) can inflame the bladder.
Symptoms
The symptoms are very distinctive:
- Urgency to urinate with a high frequency.
- Cloudy urine with a strong smell.
- Stinging sensation when urinating.
- Pain and/or abdominal pressure.
- Occasional haematuria (blood in the urine).
- Occasional fever.
- Nausea and occasional vomiting.
Treatment
The main treatment is based on antibiotics, and to determine the appropriate treatment it will often be necessary to do a "urine culture" which identifies the agent causing the infection.
Drink a lot of water and urinate often: This helps to flush out the infection.
Chronic cystopathies will often require an anatomopathological diagnosis, and sometimes the surgical treatments that the original pathology requires.